References
Details
COMPOSITE REBAR DESCRIPTION
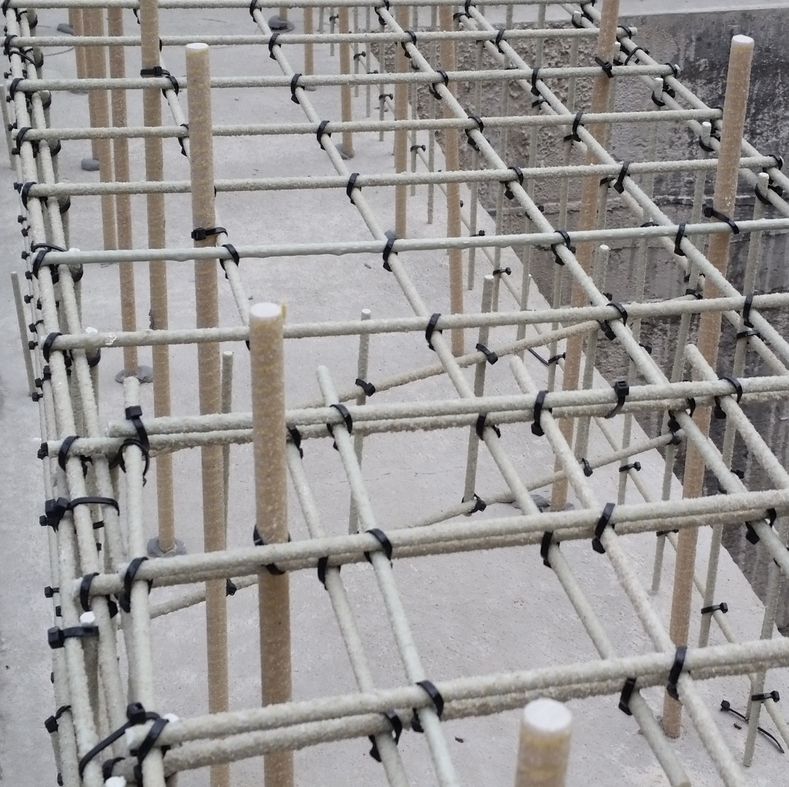
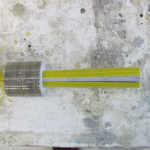
We produce several basic types of composite rebar for different applications. The reinforcing fibers are glass or carbon, all laid longitudinally. Fiber types include glass (AR or E type), carbon, and others (e.g. basalt). The proportion of fiber in the finished material is 75-80% by weight. The matrix is vinylester, polyester, or epoxy resin. The surface is spiral-wound to maintain its shape; above this is a layer of silicate sand suspended in resin to improve bonding with the surrounding concrete.
- Additional external reinforcement (PREFACARB) for additional strengthening
- Additional reinforcement placed near the surface (PREFA REBAR, PREFEN FS, FB)
- Internal reinforcement (PREFA REBAR) for new structures
PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS AND
KEY FEATURES
- Chemically stable: Composite rebar resists chemical corrosion and is suitable for chemical production facilities and wastewater treatment plants. Composites do not react with chlorides and have minimal interaction with acidity (pH).
- Composites do not corrode in air, and as such do not need to be insulated from it. This enables material savings, as the final structural element is less massive.
- Composite materials have minimal thermal conductivity and do not form thermal bridges.
- Composite materials are electrically non-conductive and do not corrode when exposed to wandering current.
- Composite materials are transparent to electromagnetic waves; i.e., composite structures do not degrade EM signals. Composite rebar can be used in structures adjacent to high-voltage power lines and transformers.
types of materials
- Glass / polyester – temporary reinforcement
- Glass / vinyl ester – long-term application
- Carbon / vinyl ester – long-term demanding applications
- Carbon / epoxy – long-term demanding applications
Types of reinforced structures
- Concrete structures
- Masonry
- Wooden construction
| System | PREFEN FS, FB | PREFA REBAR | PREFACARB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Glass | Carbon/Glass | Glass | Rods | Web | |
| Tensile strength (mean) [MPa] | 3,000 | 1,000 | 1,200 | 1,000 | 3,000 | 4,800 |
| Elastic modulus (mean) [GPa] | 155 | 55 | 70 | 50 | 155 | 230 |
NOTE: By selecting suitable materials, mechanical properties can be increased.
The product is patented: Utility models 17951, 17 847, 19307, Patent 302103
![Back to homepage [PREFA KOMPOZITY,a.s. logo]](https://www.prefa-kompozity.cz/en/wp-content/themes/prefakompozityen/images/prefa-kompozity-logo-new.png)